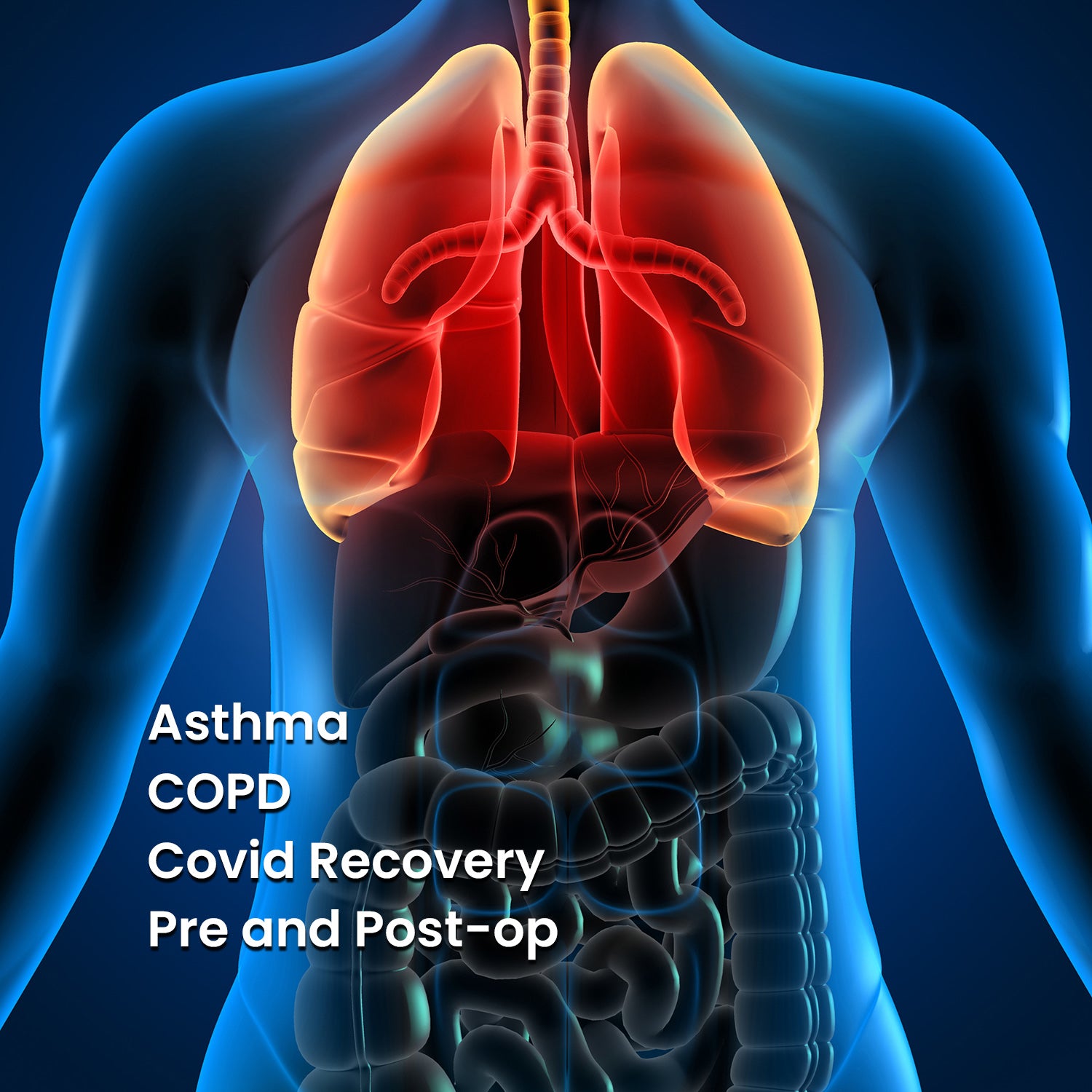
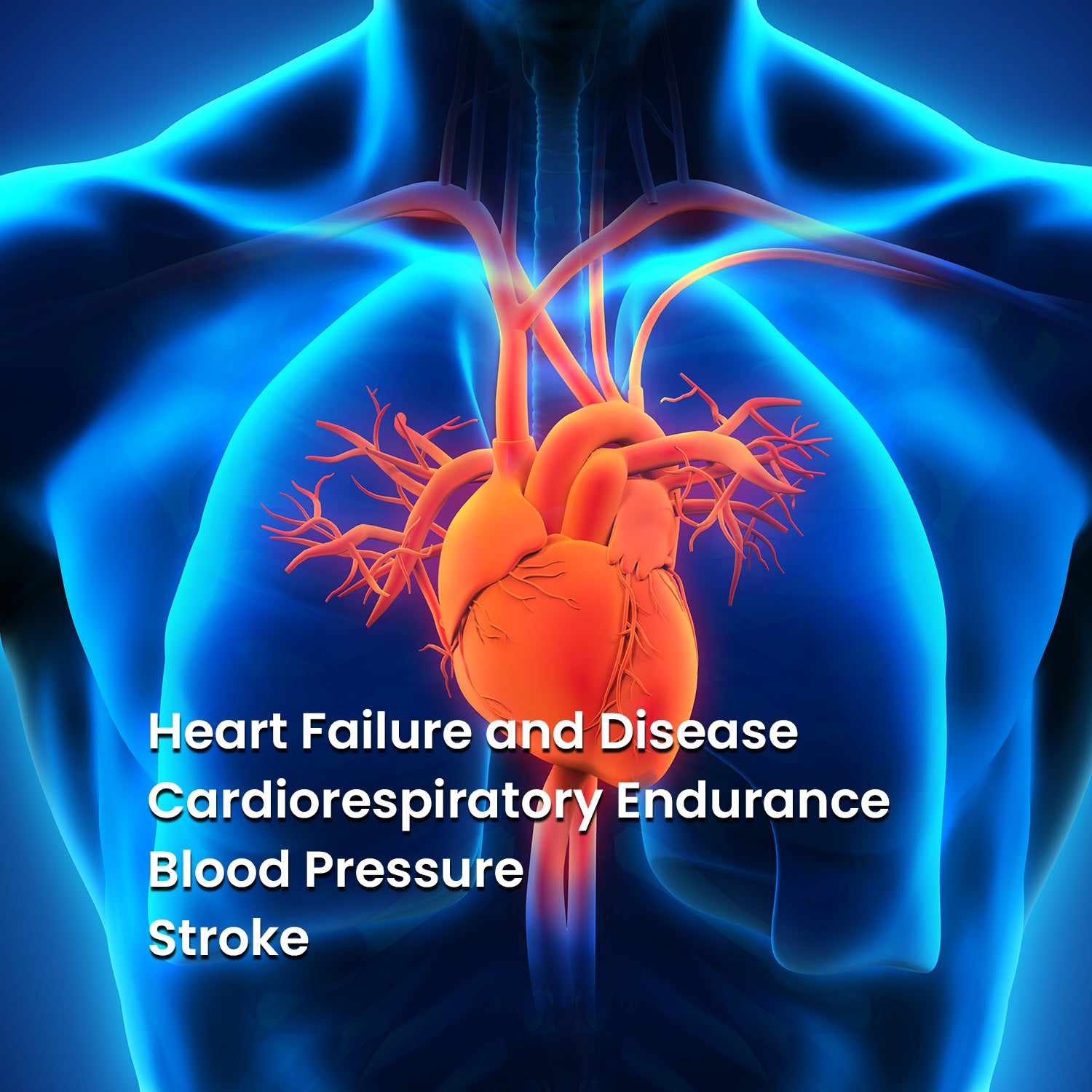
It’s a natural thing: breathe in, breathe out... But, there actually is a wrong and right way to get oxygen into our system through our lungs.
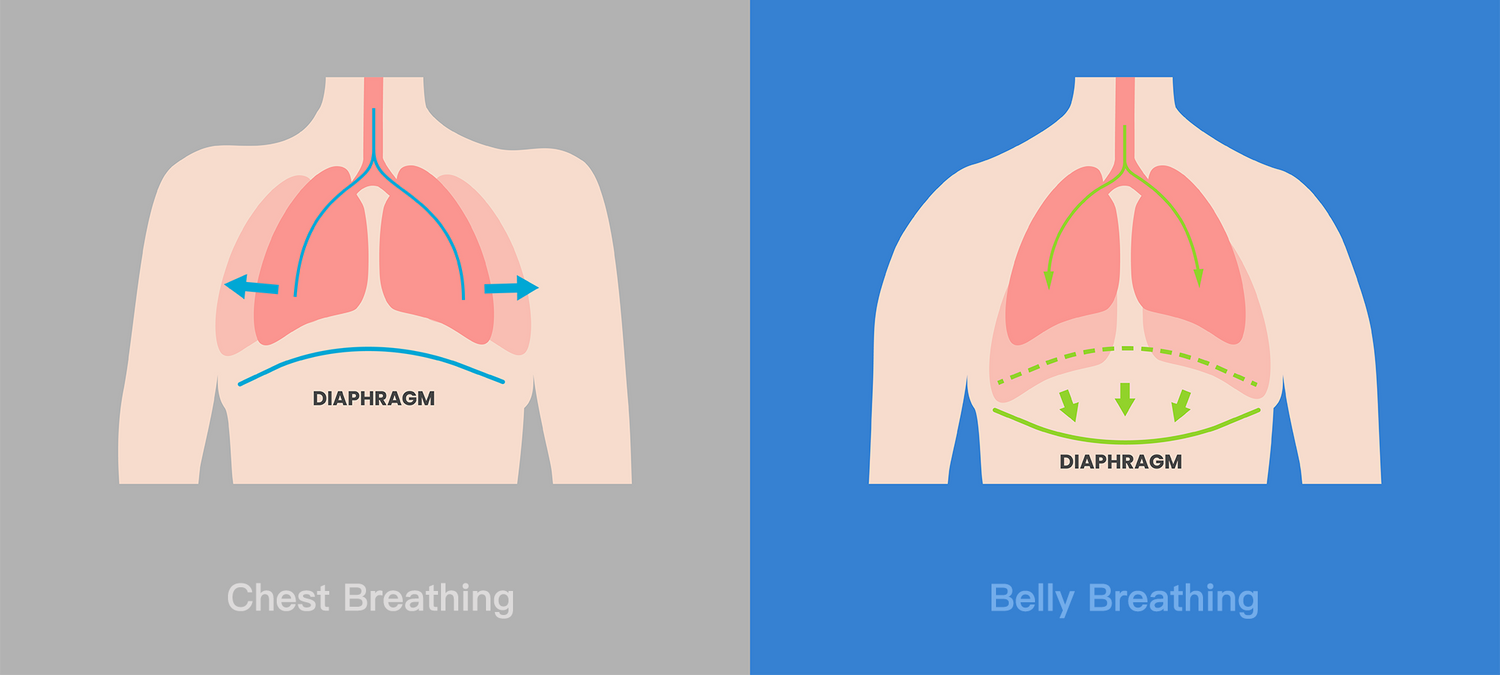
In today’s modern world, many of us excessively use chest breathing which causes overuse of the neck musculature and can lead to pain syndromes in the neck, shoulders, and upper back.. To keep our body and mind operating in an optimum state, we need to learn to breathe correctly.
And like our other muscles, our breathing muscles can be trained to be stronger.
Who can benefit from breathing exercises?

Sport & Art Performance
- Fitness
- Swim, Bike, Run
- Football, Rugby, Golf
- Obstacle Course Racing
- Dance, Music, Singing
Why Breathing Exercises Helps?
Correct Breathing Way
Most people reply too much on chest breathing instead of belly breathing. Chest breathing will bring more burden to arm swinging and lead to the instability of the arm swinging as the thoracic movement will obviously drive the shoulders up and down. Belly breathing will not only improve the respiratory efficiency but also help to enhance the core stability, thus creating good conditions for arm swinging.
Activate Diaphragm and Increase VO2Max
VO2Max means the maximum amount of oxygen your body can absorb and function at its best. As
your oxygen intake increases, your performance in any aerobic endurance exercise will improve. The more active the diaphragm, the more oxygen you breathe.
Improve the Capacity of Sputum Excretion
Strengthen respiratory muscles to improve the capacity of sputum excretion, loosen the sputum in the trachea and lungs and easy to cough up.
Improve Core Strength
When exhaling, you must be able to fully exhale the air from the lungs, which requires that the core muscles can be tightened quickly and well. Only when the core is
tightened can the diaphragm be fully jacked up and the air in the lungs be fully expelled. Breathing exercises allow abdominal breathing to flow naturally into the body, tightening the core and keeping the speed up during the sprint.
About Breathing Exercises
What is respiratory muscle training (RMT)?
Respiratory Muscle Training (RMT) can be defined as a technique that aims to improve the function of the respiratory muscles through specific exercises. RMT may consist of Inspiratory Muscle Training (IMT) or Expiratory Muscle Training (EMT) or a combination of the two.
Most versatile method: Resistance Training - inspiratory pressure threshold loading (IPTL) is by far the most commonly used, researched and validated method of RMT.
What is inspiratory muscle training (IMT)?
IMT is a form of resistance (weight) training which strengthens the muscles that you use to breathe. When these muscles are strengthened regularly for a period of a few weeks they adapt, becoming stronger and being able to work for longer. You will also be able to exercise more without getting so breathless.
What is inspiratory vital capacity (IVC)?
Inspiratory vital capacity (IVC) represents the maximal intake of oxygen in proportion to the maximal expiratory level serving as a subset of forced vital capacity (FVC) that measure the size of the lungs. Spirometry is the clinical standard in assessing lung functionality by making comparative analyses between lung size and airflow, reflecting inspiration (breathing in) and expiration (breathing out) variables.
What is the normal range of inspiratory capacity in mL?
For an adult, a normal inspiratory capacity is about 3 liters, or about 3,000 mL. A number of physiological factors like age, gender, height and ethnicity effect lung volumes.
Learn more: Inspiratory Capacity Chart
How to maintain the health of respiratory system?
- Exercise regularly to keep your lungs healthy.
- Eat a healthy diet with lots of fruits and vegetables and drink water to stay hydrated
- Avoid pollutants that can damage your airways, including secondhand smoke, chemicals and radon (a radioactive gas that can cause cancer). Wear a mask if you are exposed to fumes, dust or other types of pollutants for any reason.
- Don't smoke.
- Prevent infections by washing your hands often and getting a flu vaccine each year.
What conditions affect the respiratory system?
Allergies
Breathing in proteins like dust, mold, and pollen may lead to respiratory allergies for some people, causing inflammation in their airways.
Asthma
Asthma, a chronic condition, involves inflammation in the airways, which can result in breathing difficulties.
Infection
Respiratory infections like the flu (influenza) or a cold can result in pneumonia (lung inflammation) or bronchitis (inflammation of the bronchial tubes).
Disease
Respiratory disorders encompass conditions such as lung cancer and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). These illnesses can impair the respiratory system's capacity to transport oxygen throughout the body and eliminate waste gases.
Aging
Lung capacity decreases as you get older.
Damage
Breathing problems can result from damage to the respiratory system.