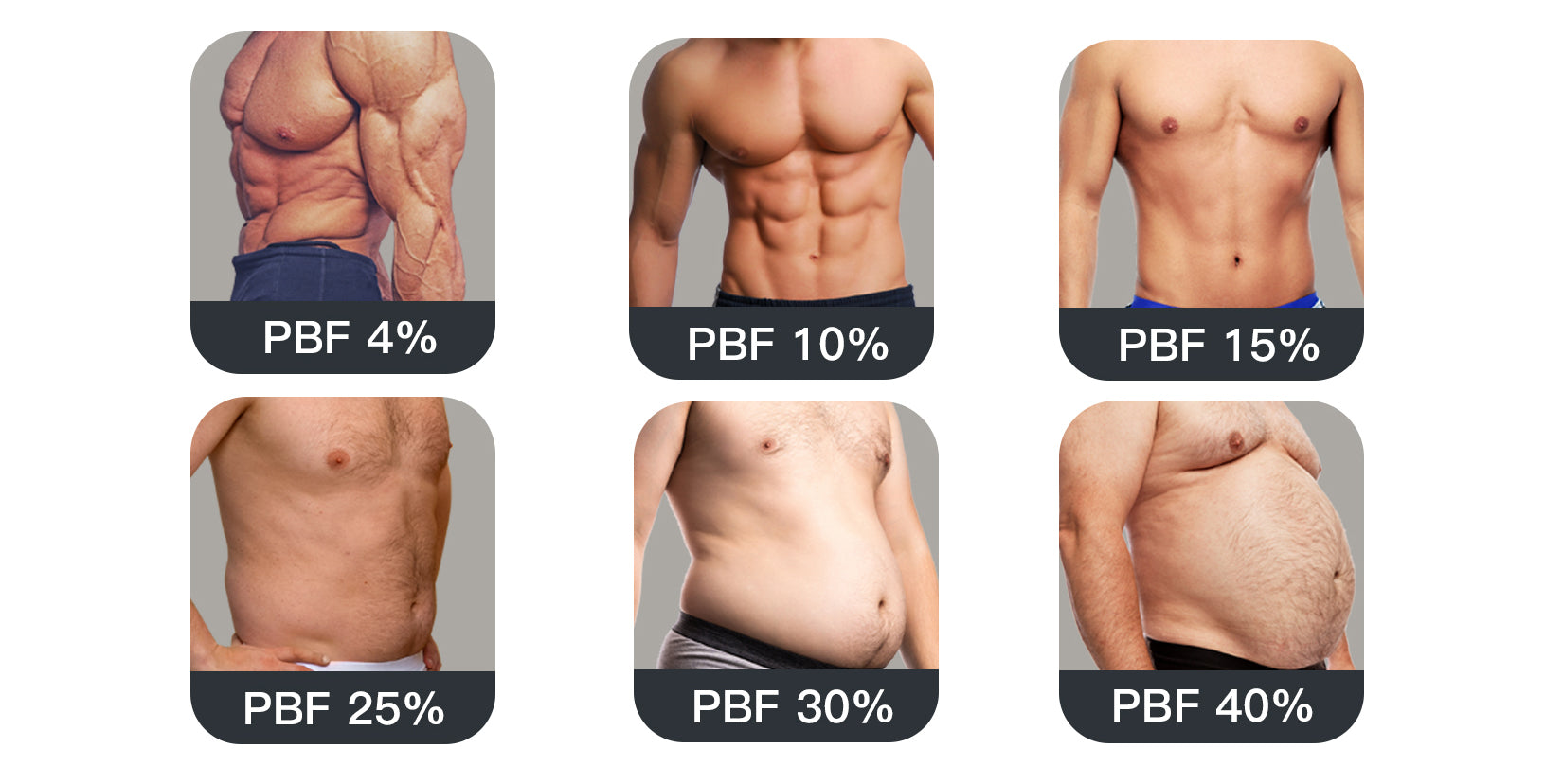
Understanding body composition is essential for those seeking to enhance their health, fitness, and overall well-being. Rather than focusing solely on weight, body composition provides a detailed breakdown of the different components that make up your body. This blog will delve into the various aspects of body composition, its significance, and how modern technology, such as the BodyPedia Body Composition Scale, can assist in tracking and improving it.
What is Body Composition?
Body composition refers to the percentages of fat, bone, water, and muscle in the human body. Two individuals of the same height and weight might have completely different body compositions, resulting in different health statuses and physical appearances. Here are the primary components:
- Body Fat: This includes essential fat, which is necessary for normal physiological functions, and storage fat, which accumulates under the skin and around internal organs.
- Muscle Mass: Refers to the amount of muscle in the body, including skeletal muscles, smooth muscles, and cardiac muscles.
- Bone Density: Indicates the amount of mineral matter per square centimeter of bones.
- Water Content: Represents the amount of water in the body, essential for various bodily functions.
Importance of Body Composition
- Health Indicators: High body fat percentage, especially visceral fat, can increase the risk of various health issues like cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, and certain cancers.
- Fitness Assessment: Athletes and fitness enthusiasts use body composition to tailor their training and nutrition plans for optimal performance.
- Weight Management: Helps in distinguishing between weight loss from fat and muscle, guiding effective weight management strategies.
- Monitoring Progress: Tracking changes in body composition over time can provide a more accurate picture of health and fitness improvements than weight alone.
Methods to Measure Body Composition
Several methods are available to measure body composition, each with its advantages and limitations:
- Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis (BIA): This method uses a small electrical current to measure the resistance of body tissues, providing estimates of body fat, muscle mass, and water content. Devices like the BodyPedia Smart Body Composition Scale employ advanced BIA technology for high accuracy.
- Dual-energy X-ray Absorptiometry (DEXA): Often considered the gold standard, DEXA scans provide detailed body composition analysis but are expensive and typically available only in medical settings.
- Skinfold Measurements: Involves using calipers to measure the thickness of subcutaneous fat at specific body sites. While inexpensive, it requires skill for accurate measurements.
- Hydrostatic Weighing: Measures body density by comparing a person's weight on land to their weight underwater. It’s accurate but not easily accessible.
- Air Displacement Plethysmography: Similar to hydrostatic weighing but uses air displacement to measure body volume and density. It’s less cumbersome but still requires specialized equipment.
Traditional BIA Technology vs. Advanced BIA Technology
Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis (BIA) technology has evolved significantly over the years, leading to the development of both traditional and advanced BIA systems.
Traditional BIA Technology
Traditional BIA technology typically uses four electrodes, with sensors placed on the footpads of the scale. This setup measures the impedance of the lower body only. While it provides a basic assessment of body composition, it has notable limitations:
- Limited Accuracy: Since it only measures the lower body, the results may not accurately reflect the composition of the upper body.
- Less Detailed: Traditional BIA cannot distinguish between different types of body mass, such as fat and muscle, as effectively as advanced methods.
Advanced BIA Technology
Advanced BIA technology, on the other hand, often employs eight electrodes, with sensors for both the hands and feet. This allows for a full-body analysis, significantly enhancing the accuracy and detail of the measurements:
- Comprehensive Analysis: By measuring impedance through both the upper and lower body, advanced BIA provides a more complete and accurate assessment of overall body composition.
- Enhanced Accuracy: It can differentiate between fat, muscle, and body water more precisely, offering detailed insights into your body’s makeup.
- Better Health Tracking: With more accurate and detailed data, advanced BIA is a superior tool for monitoring changes in body composition, helping you track fat loss, muscle gain, and overall health progress more effectively.
The Bodypedia Body Composition Scale leverages this advanced eight-electrode BIA technology, delivering highly accurate and comprehensive body composition measurements. This ensures you have the best tools at your disposal to monitor and achieve your health and fitness goals.
Practical Applications and Benefits
- Tailored Fitness Plans: By understanding body composition, users can create more effective fitness plans that focus on building muscle and reducing fat in targeted areas.
- Nutritional Adjustments: Detailed insights into body composition can guide dietary changes to support muscle growth and fat loss.
- Motivation and Accountability: Tracking progress with precise data can boost motivation and help maintain accountability in a fitness journey.
- Health Monitoring: Regular monitoring can detect early signs of health issues related to body composition, allowing for timely interventions.
How to Improve Your Body Composition
The goal for most people is to decrease body fat and increase muscle mass. While many know the importance of proper nutrition and exercise, the challenge often lies in knowing where to begin. Here are your first steps:
1. Assess
-
Measure Your Body Composition: Start by accurately measuring your body composition using a reliable tool like the Bodypedia Body Composition Scale.
-
Set a Goal: Define clear and achievable body composition goals based on your current measurements.
2. Nutrition
- Caloric Needs: Determine how many calories you need to achieve your personal goal. You will need more calories for muscle growth and fewer calories for fat loss.
-
Macronutrient Balance: Ensure you are getting enough macronutrients (proteins, fats, and carbohydrates) from a variety of foods.
- Protein: Focus on protein intake, as it is essential for muscle growth and fat loss.
- Variety: Include a range of nutrient-dense foods in your diet such as fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, whole grains, and healthy fats.
3. Exercise
- Physical Activity: Engage in regular physical activity, which is crucial for everyone.
- Resistance Training: Incorporate resistance training (such as weightlifting or bodyweight exercises) to challenge your muscles and help them grow stronger.
- Cardio Workouts: Add cardiovascular exercises to help burn calories and improve heart health.
- Flexibility and Balance: Activities like yoga or Pilates can enhance your flexibility and balance, contributing to overall fitness.
By starting with these steps, you can create a solid foundation for improving your body composition and achieving your health and fitness goals.
Summary
Body composition analysis is a vital tool for anyone serious about improving their health and fitness. Devices like the BodyPedia Smart Body Composition Scale make it easier than ever to obtain accurate and comprehensive body metrics at home. By leveraging such technology, individuals can make informed decisions, set realistic goals, and track their progress effectively, ultimately leading to better health outcomes and enhanced well-being.